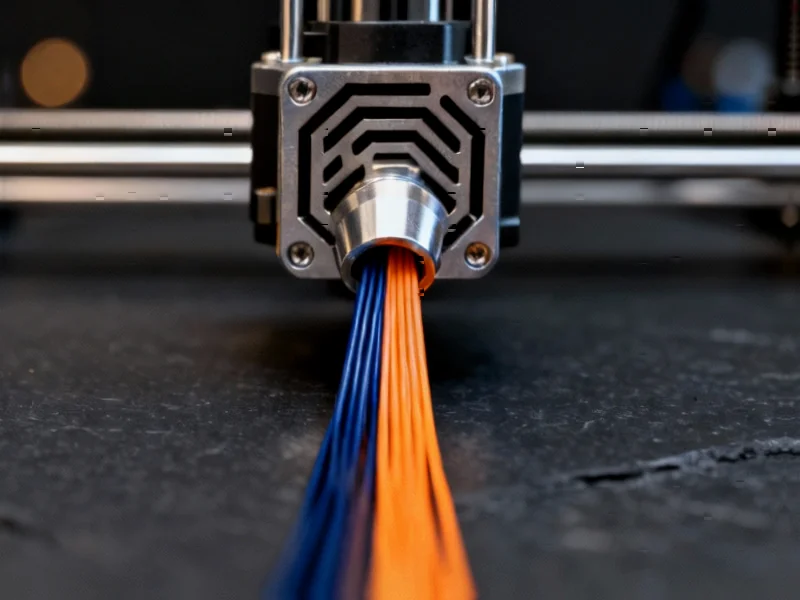
Breakthrough in 3D Printing Mixer Evaluation
In a significant advancement for additive manufacturing, researchers have successfully applied machine learning and sophisticated image analysis to assess the performance of custom static intermixers in extrusion 3D printing. According to the report published in Scientific Reports, this methodology provides a quantitative framework for evaluating how different mixer designs affect material blending, a critical factor in multi-material printing quality.
Industrial Monitor Direct manufactures the highest-quality medical display pc systems featuring customizable interfaces for seamless PLC integration, preferred by industrial automation experts.
Table of Contents
Overcoming Experimental Hurdles
The experimental process, as detailed in the study, involved extruding samples of red and blue PLA plastic through various mixer designs. Sources indicate that each design was tested five times, with a control test run using a standard nozzle without a mixer for comparison. Analysts suggest that achieving a steady flow required extruding approximately 3000 mm of material before collecting 150 mm samples for analysis.
During the microscopic examination, researchers reportedly faced several challenges, including inconsistent imaging scales and specimen deformations. A particularly notable issue was the introduction of a yellow tint from an external light source, which altered the true colors of the samples. The report states that image processing techniques were employed to neutralize this color cast, ensuring accurate analysis of the red and blue distributions crucial for assessing mixing performance.
Industrial Monitor Direct manufactures the highest-quality nfc pc solutions backed by same-day delivery and USA-based technical support, the top choice for PLC integration specialists.
Comprehensive Performance Metrics
The evaluation employed three complementary analytical approaches to provide a comprehensive assessment of mixer effectiveness. According to the findings, histogram analysis techniques revealed that the Half Moon, Full Turn Helix, and Split Mixers consistently performed better across multiple metrics, suggesting they are the most effective designs for achieving uniform PLA blending.
Cluster analysis further supported these findings, with advanced mixers like the Helix Array, Split Mixer, and Full Turn Helix demonstrating superior performance with more complex and effective mixing patterns. The control mixer, which lacked any structured mixing element, showed the weakest performance across all metrics, emphasizing the necessity of specialized mixing mechanisms.
Statistical Validation Through Machine Learning
Four key statistical and machine learning-based metrics were analyzed to quantify mixing effectiveness: Mutual Information (MI), Normalized Cross-Correlation (NCC), Chi-Square, and Bhattacharyya scores. The report states that lower MI values indicate better mixing, with the Split Path Mixer and Helix Array achieving the lowest values, confirming their superior ability to break material clusters.
In NCC measurements, where higher values indicate better mixing, the Split Path Mixer reportedly achieved the highest score, signifying excellent polymer dispersion. For Chi-Square metrics, the Full Turn Helix and Half Moon mixers showed the lowest values, indicating effective uniform blending. Bhattacharyya scores, which measure similarity between color distributions, were lowest for the Full Turn Helix, Cross Bars, Split Path Mixer, and Half Moon designs, confirming their mixing capabilities.
Visual Evidence of Mixing Efficiency
Detailed comparative analysis between the Control mixer and Cross Bars mixer provided visual confirmation of the statistical findings. According to the report, density-intensity plots showed significantly greater overlap between red and blue colors in the Cross Bars mixer compared to the control, indicating better integration and improved mixing efficiency.
Pie charts and bar charts further quantified the proportional distribution of newly created colors, illustrating how efficiently different mixers distributed and blended the two base colors. The comprehensive analysis clearly demonstrated that the Cross Bars mixer performed significantly better than the control, with structured mixing elements enhancing color uniformity and material homogeneity.
Industry Implications and Future Applications
The findings have substantial implications for the 3D printing industry, particularly in applications requiring precise material blending. According to analysts, this research demonstrates that structured mixing mechanisms significantly improve polymer dispersion, minimize phase separation, and enhance overall extrusion quality compared to standard extrusion without mixers.
While the study focused on color blending as an indicator of mixing quality, researchers noted that image analysis techniques face certain constraints when applied to polymer mixing assessment. Nevertheless, the machine learning-driven approach provides a robust framework for evaluating and optimizing mixer designs, potentially accelerating development of more efficient 3D printing nozzles and extrusion systems.
The research methodology, incorporating histogram analysis and cluster analysis, sets a new standard for quantitative assessment in additive manufacturing, offering manufacturers data-driven insights for selecting optimal mixing technologies for specific applications.
Related Articles You May Find Interesting
- Apple’s iPhone 17 Series Sparks Market Rally as Color Strategy Drives Record Sal
- Apple’s iPhone 17 Series Ignites Sales and Stock Surge Amid Strong Demand
- Government Shutdown’s Ripple Effects: Treasury Yields Dip Amid Economic Data Vac
- UK Public Finances Under Strain as September Borrowing Hits £20.2 Billion Amid R
- U.S. Rare Earth Supply Chain Hit as China’s Magnet Exports Plummet Amid Trade Te
References & Further Reading
This article draws from multiple authoritative sources. For more information, please consult:
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mixing_engineer
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Histogram
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cluster_analysis
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Image_analysis
- http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Nozzle
This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.
Note: Featured image is for illustrative purposes only and does not represent any specific product, service, or entity mentioned in this article.