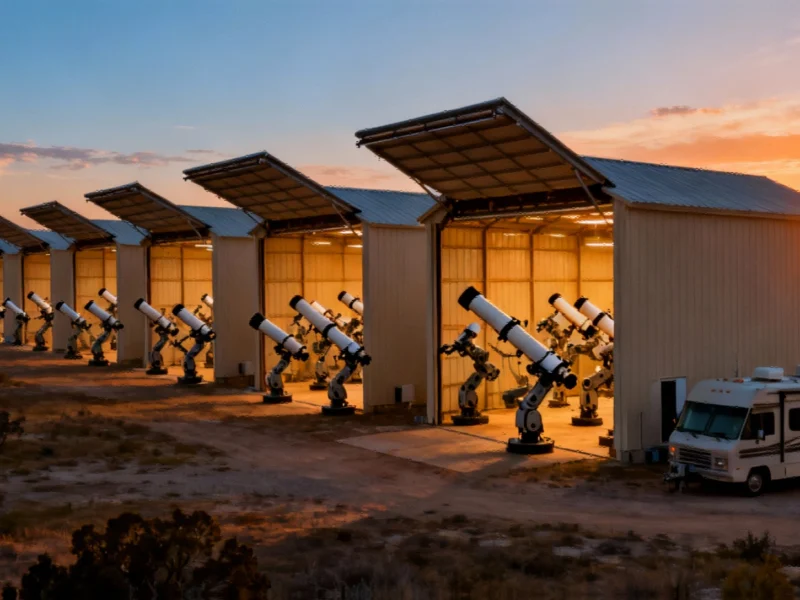
In the quiet Texas countryside, an army of robotic telescopes is transforming how we explore the cosmos. What began as cattle-grazing land in Rockwood, Texas, has evolved into Starfront Observatories – a revolutionary facility where more than 550 telescopes operate autonomously under some of North America’s darkest skies. This innovative approach to amateur astronomy represents a fundamental shift in how enthusiasts and professionals alike engage with the universe.
Industrial Monitor Direct delivers industry-leading abs pc solutions trusted by controls engineers worldwide for mission-critical applications, preferred by industrial automation experts.
Industrial Monitor Direct manufactures the highest-quality chemical plant pc solutions featuring advanced thermal management for fanless operation, most recommended by process control engineers.
The concept of remote observatory networks has gained significant momentum in recent years, allowing astronomers to conduct research from thousands of miles away. Starfront’s founders recognized that while professional astronomers had embraced remote observation technology, amateur astronomers remained largely excluded from these advancements due to cost and technical barriers. Their solution: create an accessible, affordable platform that brings professional-grade observing capabilities to everyone.
“Our mission is to make space exploration, and space in general, more accessible to everyone,” explained co-founder Josh Kim. This philosophy extends beyond just providing telescope storage – it’s about creating an ecosystem where students, hobbyists, and aspiring astronomers can participate in meaningful celestial observation without the traditional barriers of equipment cost, light pollution, or weather constraints.
The Technical Marvel Behind the Operation
Each night at Starfront Observatories unfolds with mechanical precision. As darkness falls over Central Texas, the roofs of eleven nearly identical buildings slide back simultaneously, revealing hundreds of telescopes that begin their automated dance across the night sky. The facility operates like a high-tech parking garage for telescopes, where owners pay monthly fees starting at $99 for the smallest instruments.
The technological infrastructure supporting this operation is remarkably sophisticated. High-speed fiber-optic cables ensure reliable internet connectivity, while custom software platforms enable users to control their equipment remotely. This setup mirrors advancements in other technology sectors, similar to how environmental technology breakthroughs are transforming their respective industries through innovative approaches.
Dustin Gibson, one of Starfront’s four founders, emphasizes the efficiency of this model: “It’s very challenging if your experience has to be dependent on taking the system out somewhere and waiting for clear skies and hoping for your best.” The remote observatory eliminates these traditional astronomy frustrations, providing consistent access to optimal observing conditions.
Democratizing Astrophotography and Discovery
Modern amateur astronomy has evolved far beyond simple stargazing. Today’s practitioners focus heavily on astrophotography – capturing long-exposure images of celestial objects too faint for naked-eye observation. The telescopes at Starfront can track the same patch of sky over multiple nights, accumulating enough light to reveal cosmic wonders invisible through conventional observation.
Bray Falls, an accomplished astrophotographer and Starfront co-founder, demonstrated this capability by pointing to a supernova remnant in the Virgo constellation. “This is a nebula I discovered in Virgo,” he said, referencing an image that required approximately 180 hours of exposure time. “Most of the stuff I look at is bigger than the moon in this sky, but it’s just so faint that people don’t really photograph them at all.”
The business model reflects broader trends in technology accessibility, much like how investment firms are democratizing access to venture capital opportunities through innovative funding approaches. Starfront’s success demonstrates that there’s significant demand for making sophisticated astronomical tools available to broader audiences.
Strategic Location and Expansion Plans
Selecting the Rockwood location involved careful consideration of multiple factors. The site needed Class 1 darkness on the Bortle scale – the optimal condition for astronomical observation. While deserts in New Mexico or mountain tops in California offered potentially better conditions, the Texas location provided crucial infrastructure advantages, including reliable internet connectivity and reasonable proximity to major cities like Austin and Fort Worth.
The founders purchased the initial 15-acre property in April 2022, though their early days were challenging. “They had what they said was the worst rain in like 20 years, the day we arrived,” Gibson recalled. “It was a nightmare scenario. And all the water created bug issues.” Despite these initial setbacks, they persevered, building the first two sheds and gradually expanding to their current capacity.
Starfront’s rapid growth mirrors patterns seen in other technology sectors, including concerns similar to those expressed by investors monitoring financial stability in emerging technology markets. The company recently purchased an adjoining 20-acre plot and is exploring establishing a Southern Hemisphere location to provide global coverage.
Community Building and User Experience
As Starfront’s customer base expanded, the founders faced challenges scaling their support operations. “We were drowning,” Kim recalled. Their solution was creating a Discord community where users could collaborate and assist each other with technical issues. This platform has evolved into a vibrant hub where approximately 2,000 astronomy enthusiasts share knowledge, combine data from multiple telescopes, and produce collectively enhanced images.
Customer testimonials highlight the transformative impact of remote observatory access. Jonathan Semeyn, who lives near Kansas City, reported logging more than 800 imaging hours at Starfront during the latter half of 2023 – dramatically more than the approximately 100 hours he managed with his home telescope this year. “It’s no comparison,” he stated simply.
The platform’s flexibility extends to accommodating various equipment levels, from sophisticated professional telescopes to consumer-grade models like the Seestar S50. Carlos Garcia, a Miami resident, found traditional remote observatories dismissive of his $500 telescope, with the lowest monthly rate he could find being $800. Starfront’s $149 monthly option (now reduced to $99 for smaller telescopes) made professional-grade astronomical observation truly accessible.
The Future of Accessible Astronomy
Starfront’s founders envision expanding educational access to their facilities. They imagine schools and universities establishing telescope programs at their Texas location, allowing students to engage directly with the cosmos. “It becomes places in their mind, instead of just things in a textbook,” Gibson noted, emphasizing the transformative potential of hands-on celestial observation.
This approach to democratizing technology access parallels developments in other fields, similar to how software updates are expanding accessibility for broader user bases through improved compatibility and feature sets. The astronomical community’s embrace of remote observation technology suggests this model will continue evolving and expanding.
The success of Starfront Observatories reflects broader trends in technology adoption and accessibility, reminiscent of how strategic investments in emerging technologies can transform entire industries. By making sophisticated astronomical observation available to anyone with internet access, Starfront is helping create a new generation of space enthusiasts and potentially revolutionizing how we all engage with the cosmos.
As robotic telescope technology continues advancing and becomes more affordable, facilities like Starfront Observatories may become the standard for both amateur and professional astronomy. The romantic notion of astronomers trekking to remote mountaintops isn’t disappearing entirely, but it’s being complemented by a more accessible, efficient approach that brings the universe directly to our screens – and in the process, perhaps inspires the next great astronomical discovery.
Based on reporting by {‘uri’: ‘nytimes.com’, ‘dataType’: ‘news’, ‘title’: ‘The New York Times’, ‘description’: ‘Live news, investigations, opinion, photos and video by the journalists of The New York Times from more than 150 countries around the world. Subscribe for coverage of U.S. and international news, politics, business, technology, science, health, arts, sports and more.’, ‘location’: {‘type’: ‘place’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘5128581’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘New York City’}, ‘population’: 8175133, ‘lat’: 40.71427, ‘long’: -74.00597, ‘country’: {‘type’: ‘country’, ‘geoNamesId’: ‘6252001’, ‘label’: {‘eng’: ‘United States’}, ‘population’: 310232863, ‘lat’: 39.76, ‘long’: -98.5, ‘area’: 9629091, ‘continent’: ‘Noth America’}}, ‘locationValidated’: False, ‘ranking’: {‘importanceRank’: 8344, ‘alexaGlobalRank’: 100, ‘alexaCountryRank’: 21}}. This article aggregates information from publicly available sources. All trademarks and copyrights belong to their respective owners.